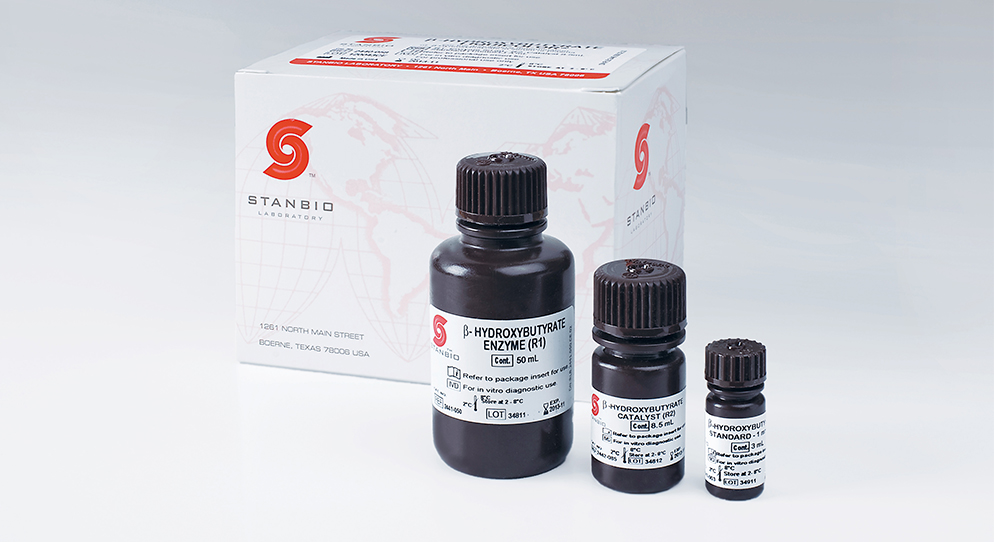
- Measurement range: β-ketone: 0.18 to 8.0 mmol/L
- Calibration Type: Single-point calibration
- Sample Type: Serum or Plasma
- Sample Volume: Varies by Analyzer
- Equipment: Any Open channel Analyzer (request for application sheet)
- About EKF
- Point-of-care Back
EKF develops point-of-care in-vitro diagnostic devices and tests, providing quick, accurate results for healthcare professionals to make rapid decisions at or near the patient’s location.
- Hematology Hemoglobin analyzers for improved diagnostics, blood donation, and anemia tests.
- DiaSpect Tm
- Hemo Control
- Hemolysis QC
- HemataStat II™
- Diabetes Care Precise analyzers for glucose, HbA1C, lactate, and B-HB measurement.
- Biosen C-Line
- Quo-Test®
- STAT-Site® WB
- Quo-Lab®
- Connectivity Connecting POC devices to IT systems, for real-time data and device management.
- EKF Link
- Women’s Health Rapid tests for pregnancy, childbirth, and mother’s milk lipid content.
- Creamatocrit Plus™
- QuPID®
- True® 20
- Sports Lactate and glucose analyzers for optimized sports training and performance.
- Lactate Scout Sport
- Biosen C-Line (Sports)
- Veterinary Care Vet analyzers for lactate, hemoglobin, and hematocrit to improve clinical decisions.
- Lactate Scout Vet
- Hemo Vet
- Hematology
- Life Sciences Back
EKF supplies high-quality reagents, enzymes, and components for research, biotech, and pharma, supporting the delivery of industrial and life sciences applications.
- Fermentation and Bio-Processing Facilities and tech that scale the fermentation and processing of biomaterials.
- Precision Fermentation
- Bio-Processing
- Diagnostic Enzymes Diagnostic enzymes for clinical, biotechnology, and industrial applications.
- Arylacylamidase (A-010)
- Beta-Hydroxybutyrate Dehydrogenase (H-010)
- Salicylate Hydroxylase (S-010)
- Contract Reagent Services Production of premium products to meet clients precise requirements.
- Reagent Formulation & Kitting
- Fermentation and Bio-Processing
- Central Laboratory Back
EKF develops devices, tests, and media for high-throughput, accurate analysis in central labs, ensuring reliable results and precise diagnostics for healthcare professionals.
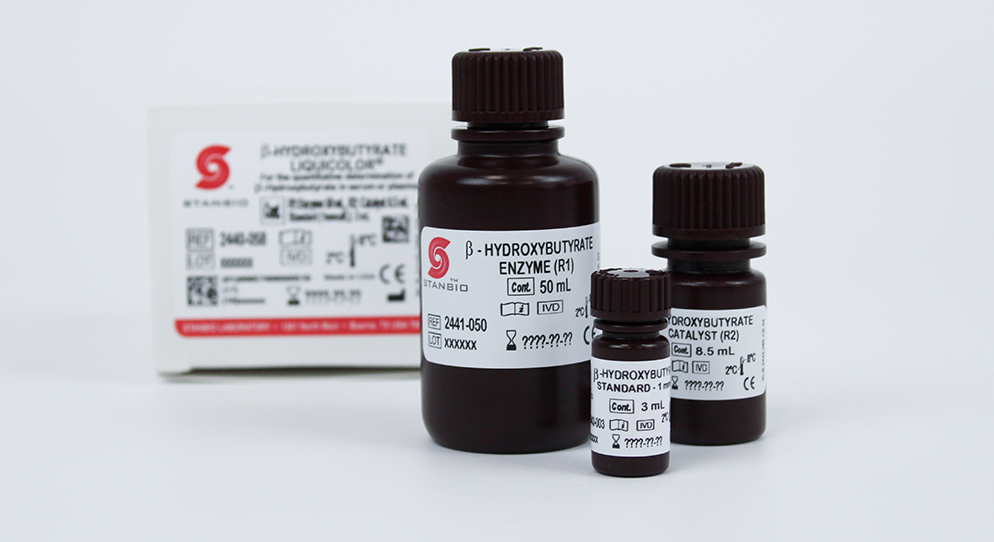
- Reagents B-HB reagents that detect ketones and monitor diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
- Beta-Hydroxybutyrate LiquiColor®
- Immunoassay Rapid tests for C-reactive protein (CRP), Rheumatoid Factor, and Syphilis.
- RaPET®
- Infectious Diseases Detect Group A Streptococcal Antigen quickly, with enhanced sensitivity for early diagnosis.
- QuStick™
- Occult Blood Test kits for Occult Blood, aiding early colorectal cancer detection affordably.
- Hema-Screen®
- Transport Media Preserve and stabilize DNA/RNA for safe transport and accurate molecular testing.
- PrimeStore®
- Lab Analyzers Using state-of-the-art tech for accurate and efficient testing with dedicated lab analyzers.
- Uri-Trak® 120M
- Clinical Chemistry Liquid-stable reagents, calibrators and controls for major brand analyzers.
- All products
- Reagents
- News & Events
- Careers
- Partner Portal
- Investors
- Contact