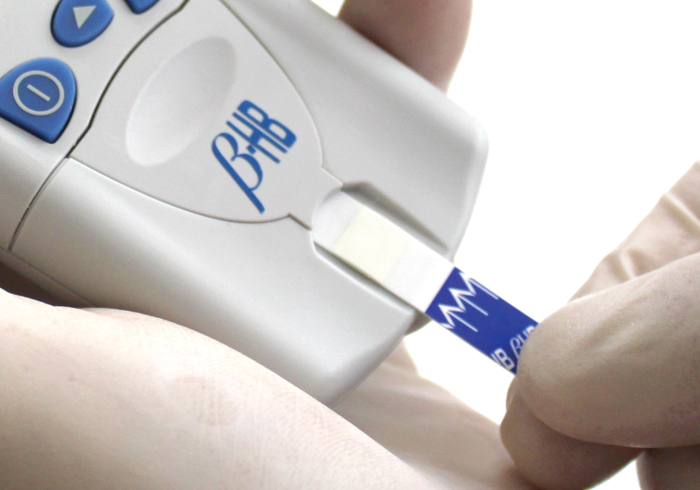
The STAT-Site® M BHB analyzer from EKF Diagnostics is used for the quantitative determination of B-Hydroxybutyrate (Beta-Hydroxybutyrate or BHB) in serum or plasma.
B-HB is used to aid the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with ketosis (also known as ketoacidosis and diabetic ketoacidosis or DKA).
Ketosis occurs when the body begins to break down its stored fats in response to a low supply of energy (glucose). This process produces the ketone BHB, which is further catabolised into acetoacetate and then into acetone.
Because BHB accounts for 78% of all ketones present in the body, and is the first one to be present during ketosis, it provides the clearest indication of a patient’s condition before and after treatment. For this reason it is a more appropriate test than traditional nitroprusside tests for acetoacetate and acetone.
The STAT-Site M BHB analyzer uses dry reagent strips to provide results in 80 seconds allowing patients displaying symptoms to be quickly diagnosed and then monitored on a regular basis.
The specificity of BHB means that patients receive a higher quality of care while reducing stays in Emergency Rooms and Intensive Care Units.
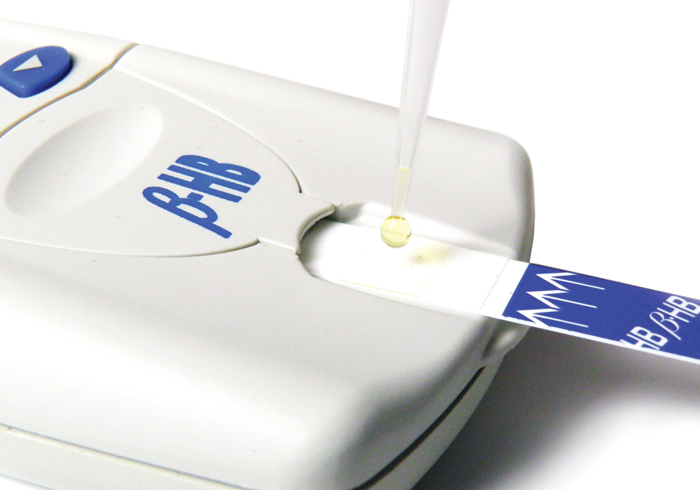

Methodology: Reflectance photometry
Principle: Beta-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
Sample Size: 10 µL
Range: 0.01 - 2.0 mmol/L (without dilution)
Calibration: Automatic (CODE Key). Lot specific CODE Key included in every box of test strips
Allows you to determine the presence and degree of ketosis by measuring blood levels of BHB.
With only 10 µl L of serum or plasma you get quantitative results in less than 80 seconds.
Knowing BHB levels offers useful information for monitoring diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in newlydiagnosed patients and for reducing time and costs in an intensive care unit.*
When the body begins to break down its stored fats in response to a low supply of energy (glucose) it produces the ketone B -Hydroxybutyrate, which is further catabolised into acetoacetate and then into acetone.
Ketones (like glucose) can be tested or monitored in either urine or blood. Many hospitals still use Acetest or Ketostix for detecting and monitoring ketosis and ketoacidosis. This nitroprusside urine method produces a qualitative assessment of ketosis and ketoacidosis by detecting both acetoacetate and acetone. However nitroprusside methods do not detect B-HB.
B-HB is a better test for ketosis and ketoacidosis than nitroprusside methods for a number of reasons:
People with type 1 diabetes may be at risk when they do not have enough insulin, a hormone the body uses to break down sugar (glucose) in the blood for energy. When the body senses glucose is not available, fat is broken down instead.
As fats are broken down, acids called ketones build up in the blood and urine. Ketones are poisonous in high levels. This condition is called ketoacidosis.
Blood glucose levels rise (usually higher than 200 mg/dL) because the liver makes glucose to try to combat the problem. However the cells cannot pull in that glucose without insulin.
Symptoms can include rapid deep breathing, dry skin and mouth, flushed face, fruity smelling breath, nausea, vomiting and stomach pain. Other symptoms that can occur are; Abdominal pain, breathing difficulty while lying down, decreased appetite, decreased consciousness, muscle stiffness and aches, dulled senses that may worsen to a coma and frequent urination and thirst that lasts throughout the day.
Copyright © 2024 | Powered by Intergage

Please note: Not all products are available in all countries. Please check availability.
Newsletter
Keep up to date with all our activities, events, exhibitions, promotions, investor news & more.